Have you ever wondered what is cell specialisation? All the biology students out there must be aware of this term. Do not worry if you don’t know the meaning of cell specialisation. In my today’s post, I will explain what is cell specialisation or differentiation in biology and why it is important. Here, I have also given the importance and examples of cell specialisation in brief. Make sure you read this post thoroughly without missing any points. Without wasting one more minute, let us now learn what is cell specialisation in detail.
What Is Cell Specialisation?
The process that occurs after cell division is called cell specialisation. Here, the newly formed cells are structurally modified. Cell specialisation allows cells to perform their function efficiently and effectively. Cell specialisation is also referred to as cell differentiation.
What Causes Cell Specialisation?
Usually, the division of stem cells into specialized cells is caused due to the change in environmental conditions. These new cells have the potential to divide into almost any cell in the body.
You must be thinking what is the cell connection between cell specialisation and stem cells. Adults are made up of somatic cells. It also contains stem cells which later on replace cells that are worn out.
As now you have understood what is cell specialisation and differentiation, let’s check out why is cell specialization important.
Importance Of Cell Specialisation
Apart from the production of cells, the process of cell specialisation is important in many other ways. You can keep on reading to find out why is cell specialization important in multicellular organisms.
- The whole process of cell specialisation is the most important during embryological development. In fact, it helps to replace old and worn-out cells during adulthood.
- This process helps in the production of cells that can produce signals that react towards a specific stimulus.
- Today, several scientists are looking into the possible uses of stem cells for treating diseases like diabetes.
- It is also found that scientists are using adult stem cells to generate more white blood cells in sufferers of leukaemia.
- Stem cells can also be used to treat certain types of breast or ovarian cancer.
- The process of cell specialisation in plants prevents further damage to living organisms.
Cell Specialisation Example
By now you have understood what is the process of cell specialisation called. We all know living organisms differ in the type of cells they are made of. Below, I have given a few examples of cell specialisation in plant and animal cells.
-
Root Hair Cells
Root hair cells are the cells located in the roots of plants. Basically, these cells’ main function is to increase the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil. Root hair cells have a large surface area which then increases the surface area for absorption. In fact, these cells also contain mitochondria that sustain high energy.
-
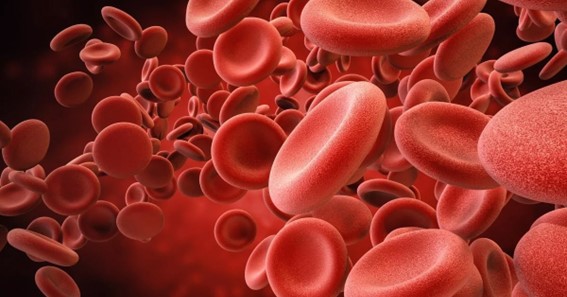
Red Blood Cells
Almost all blood cells come from undifferentiated cells in the bone marrow. These cells then develop to form specialized blood cells. For example, red blood cells are a special type of blood cell that are characterized by their lack of a nucleus. These cells have pigment hemoglobin which can combine with oxygen to form oxyhemoglobin.
-
Xylem And Phloem
Plants have specialized cells that mainly function for transport. They have a xylem that functions to transport water from the roots to the leaves. And Phloem for the transport of nutrients and organic substances from the leaves to the plant’s body. The xylem vessels are made of both living and dead cells. On the other hand, phloem is made up of only living cells.
-
Muscle Cells
Other specialized cells in animals are the muscle cell. These cells generally have a spindle-shaped cell body. It contains numerous mitochondria. Generally, muscle cells perform their function during the contraction and relaxation of muscles. These cells generate a lot of entry for locomotion.
FAQ
What Is Cell Specialisation And Why Is It Important?
Cell specializations make it possible to express fewer genes in individual cells of multicellular organisms, thus protecting genes from the damage of mutagens.
What Is Cell Specialization Examples?
Examples of specialized cells in plants: Root hair cells: specialized to absorb water and minerals from soil. Xylem cells: specialized to carry water from the roots to the leaves. Mesophyll cells: specialized to carry out photosynthesis.
How Do Cells Become Specialized?
Cells undergo a process called differential gene expression. This process allows cells to become specialized, as their structure determines their function. The process begins when a stimulus acts on an unspecialized cell (a cell that has the potential to become any cell in the body- multipotent stem cells).
Why Do Cells Become Specialised?
Humans have many different types of cells with different jobs, such as blood cells that carry oxygen and nerve cells that transmit signals to all parts of the body. Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in order to perform different functions.
What Is Meant By Cell Specialisation?
Also referred to as cell differentiation, cell specialization is the process wherein “general” or “common” cells evolve to form specific cells that have specific functions. This process is very much prevalent and most important during embryological development.
What Is Specialization In Biology?
The act of specializing, or the state of being spezialized. 2. (Science: biology) The setting spart of a particular organ for the performance of a particular function. (biology) the structural adaptation of some body part for a particular function; cell differentiation in the developing embryo.
What Is Cell Differentiation And Specialization In Biology?
Cell specialisation is the process by which cells differentiate and specialise in performing their role in a tissue, organ, and, eventually, the body. Specialised cells have distinct shapes and subcellular structures that aid in their roles. Multicellular organisms can contain hundreds of different types of cells.
You can learn much more on various topics on prozgo.com
Conclusion
From my above article, you have learned what is cell specialisation in a multicellular organism and why is it important. In simple words, cell specialisation is a process where common cells evolve to form specific cells. These specific cells have specific functions. This complete procedure is most important during embryological development. Adults are made up of somatic cells and also contain stem cells. Here, stem cells can be specialized to replace cells in the body that are worn out. By understanding what is cell specialisation, you can regenerate specific cells to do certain tasks within the body.
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit Longests
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit MainAdvantages
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit MeaningInHindiOf
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit MesBrand